Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


INC Ransomware is a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) spotted in mid-2023. It targets industries like retail, real estate, finance, healthcare, and education, primarily in the U.S. and UK. It encrypts and exfiltrates data demanding a ransom. It employs advanced evasion techniques, destroys backup, and abuses legitimate system tools at all the stages of the kill chain.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2023
First seen
:
|
8 May, 2025
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2023
First seen
:
|
8 May, 2025
Last seen
:
|

 1107
1107
 0
0
 2271
2271
 0
0

 2083
2083
 0
0
INC Ransomware is a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operated by the INC Ransom group that emerged in 2023. In mid-2024, its source code leaked to dark web and became a foundation of Lynx ransomware, the latter often referred to as “rebranding” or a variant of the former. Both employ double extortion, encrypting victims' data and threatening to leak it unless ransoms are paid.
INC Ransomware uses multiple vectors to infiltrate networks, leveraging both technical exploits and social engineering. These include phishing emails with malicious attachments or links to compromised websites, network access credentials acquired from IABs, malvertising and drive-by downloads, software vulnerabilities. INC Ransomware is used in supply chain attacks targeting third-party vendors or service providers to infiltrate larger networks (SolarWinds attack).
Once in the network, it performs privilege escalation using tools like WinPEAS and starts lateral movement using Cobalt Strike, PsExec, Mimikatz, and the like. It exfiltrates data before encrypting it with a strong algorithm (likely AES + RSA) and leaves a ransom note with payment instructions.
INC Ransom’s evasion techniques include: fileless execution, custom packers and obfuscation, delayed execution. Its living-off-the-land tactic implies the use of legitimate tools like PowerShell, WMI, and PsExec to blend in. The malware exploits SystemSettingsAdminFlows.exe to modify registry keys and disable Windows Defender.
INC Ransomware possesses significant risks since it:
Let us follow the execution chain of INC by detonating it in the safe environment of ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox and view the processes and artifacts it inducts.
View the analysis of an INC Ransomware sample.
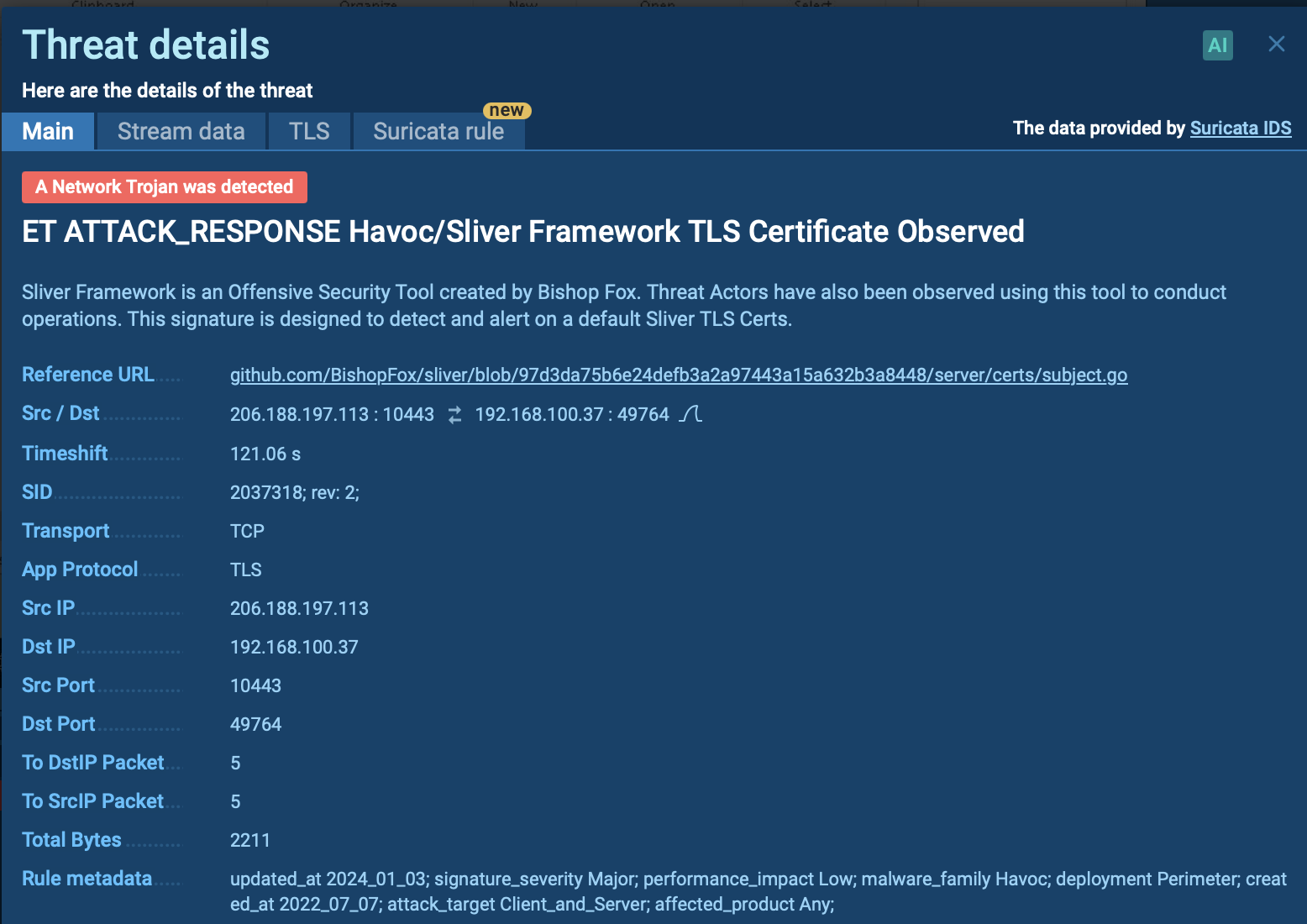
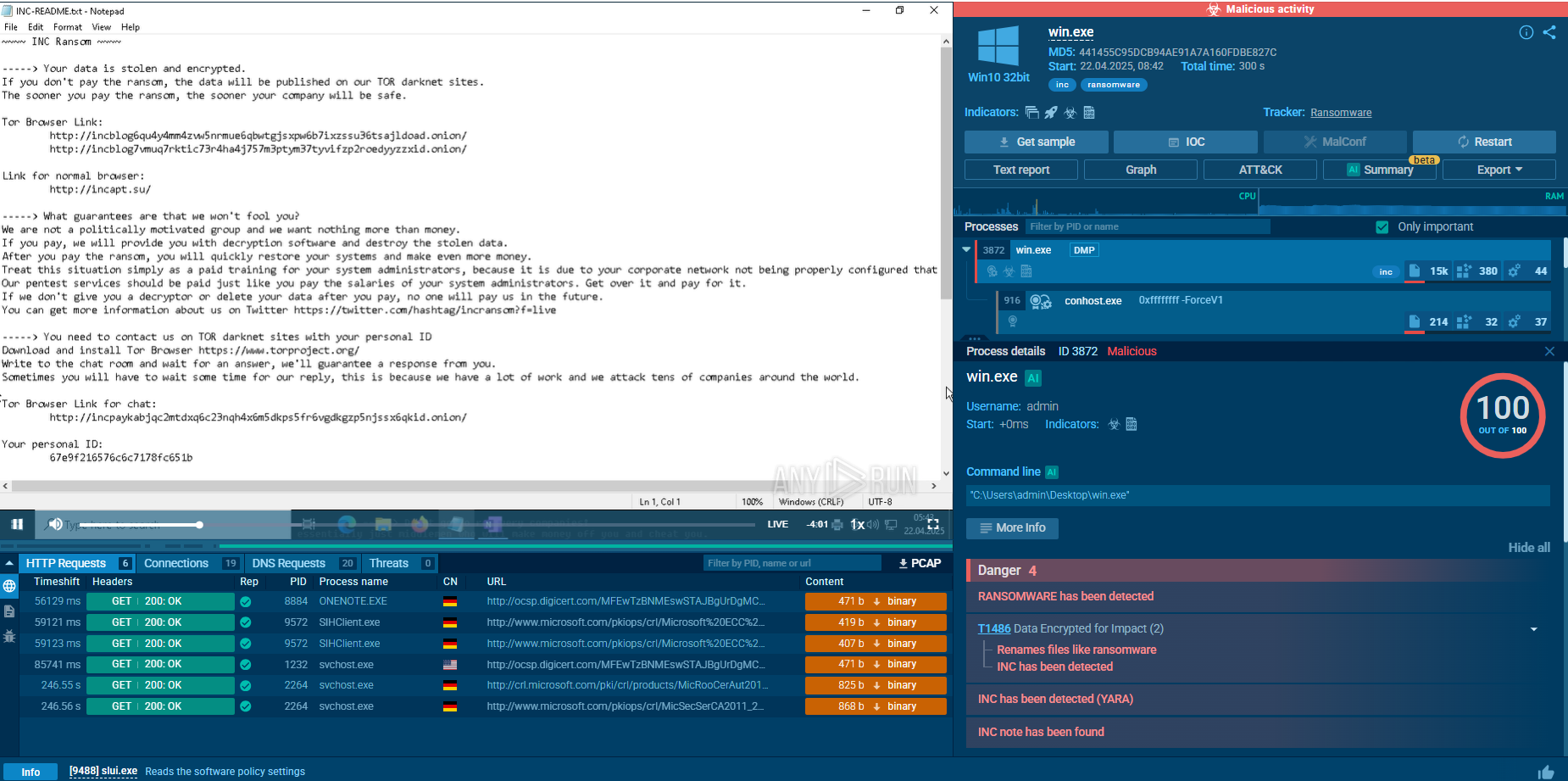 INC Ransomware sample in action in ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox
INC Ransomware sample in action in ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox
INC ransomware typically gains its initial foothold through phishing, exploitation of unpatched vulnerabilities, or credentials bought from Initial Access Brokers. Once inside, the operators run reconnaissance with commercial red-team tools and built-in Windows utilities to map the network and collect additional credentials.
They pivot laterally using living-off-the-land binaries — such as Notepad, WordPad, and others — to review files while blending in with normal activity. Next, they disable or terminate security software, backup agents, and database services via Service Control Manager APIs and custom “security-killer” tools.
Before encryption, INC tests write access by creating and truncating dummy data on target files; if files are locked, it kills the owning processes or escalates privileges to force access. Operators may also archive data with 7-Zip and exfiltrate it to cloud storage, setting the stage for double extortion. The malware then encrypts all local, mounted, and hidden volumes with AES, offering multiple modes that trade speed for thoroughness.
Finally, it drops ransom notes in .txt and .xps formats and replaces the desktop wallpaper with payment instructions and threats to leak stolen data if the ransom is ignored.
Even when two strains are as closely related as are INC Ransomware and Lynx, you can gather actionable intelligence on them separately using ANY.RUN’s services and analyze their differences and similarities to get a better understanding of malware evolution and to ensure the protection of your own system.
Start with searching by malware’s name via ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup to research more public sample analyses and gather IOCs for tuning your security systems.
 Fresh INC samples analyzed in the sandbox
Fresh INC samples analyzed in the sandbox
INC Ransomware is a dangerous RaaS using phishing, exploits, and LOTL techniques to infiltrate networks, evade detection, and turn to double extortion. It’s particularly threatening to healthcare, finance, and retail due to its disruptive potential and high ransom demands. Detection relies on EDR, behavioral analysis, and TI-driven IOCs, while countermeasures include zero-trust, backups, and patching.
Threat intelligence is critical for tracking its evolving TTPs and predicting variants like Lynx. Organizations should prioritize proactive defenses and TI integration to stay ahead of this adaptable threat.
Start with 50 requests in TI Lookup to collect IOCs on INC Ransom


.png)