Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Mars Stealer is a malware program designed to steal sensitive information from infected systems. It can access browser credentials, cryptocurrency wallets, and system information. The malware utilizes advanced evasion techniques and transmits stolen data securely through a C&C server.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2021
First seen
:
|
8 May, 2025
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2021
First seen
:
|
8 May, 2025
Last seen
:
|

 1592
1592
 0
0
 2642
2642
 0
0

 2134
2134
 0
0
First identified in June 2021, Mars Stealer is a type of malicious software primarily focused on collecting sensitive information from browsers and cryptocurrency wallets for transmission to attackers. Written in ASM/C, the malware was initially sold through Dark Web forums as a malware-as-a-service on a subscription basis. It shared similar features with other malware like Oski Stealer, Arkei, and Vidar.
While the malware appeared to have stopped functioning in 2022, with reports of unresponsive developers, evidence suggests that the original creators of Mars Stealer remain active in 2024 and continue to exploit the malware for malicious purposes.
Information theft constitutes the core focus of Mars Staler:
Mars Stealer establishes a secure connection with its Command & Control (C&C) server using SSL encryption. This encrypted communication channel allows the malware to receive instructions, download configurations and libraries, and exfiltrate stolen data without raising red flags. The information collected by the malware is compressed into a ZIP archive before being exfiltrated to the C&C server.
Mars Stealer employs various evasion techniques to escape detection and analysis. For instance, it masks its WinApi calls and encrypts strings. To prevent multiple instances of the malware from running concurrently, Mars Stealer creates a mutex object. The virus employs a custom file grabber with configuration parsing capabilities, allowing for flexible targeting of specific files and directories.
The malware includes a special feature that checks every machine before attempting infection to identify whether it is located in one of the countries that belong to the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). This likely points to the fact that the creators of Mars Stealer hail from the same region.
It’s time to have a better look at Mars Stealer by uploading its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox for closer inspection.
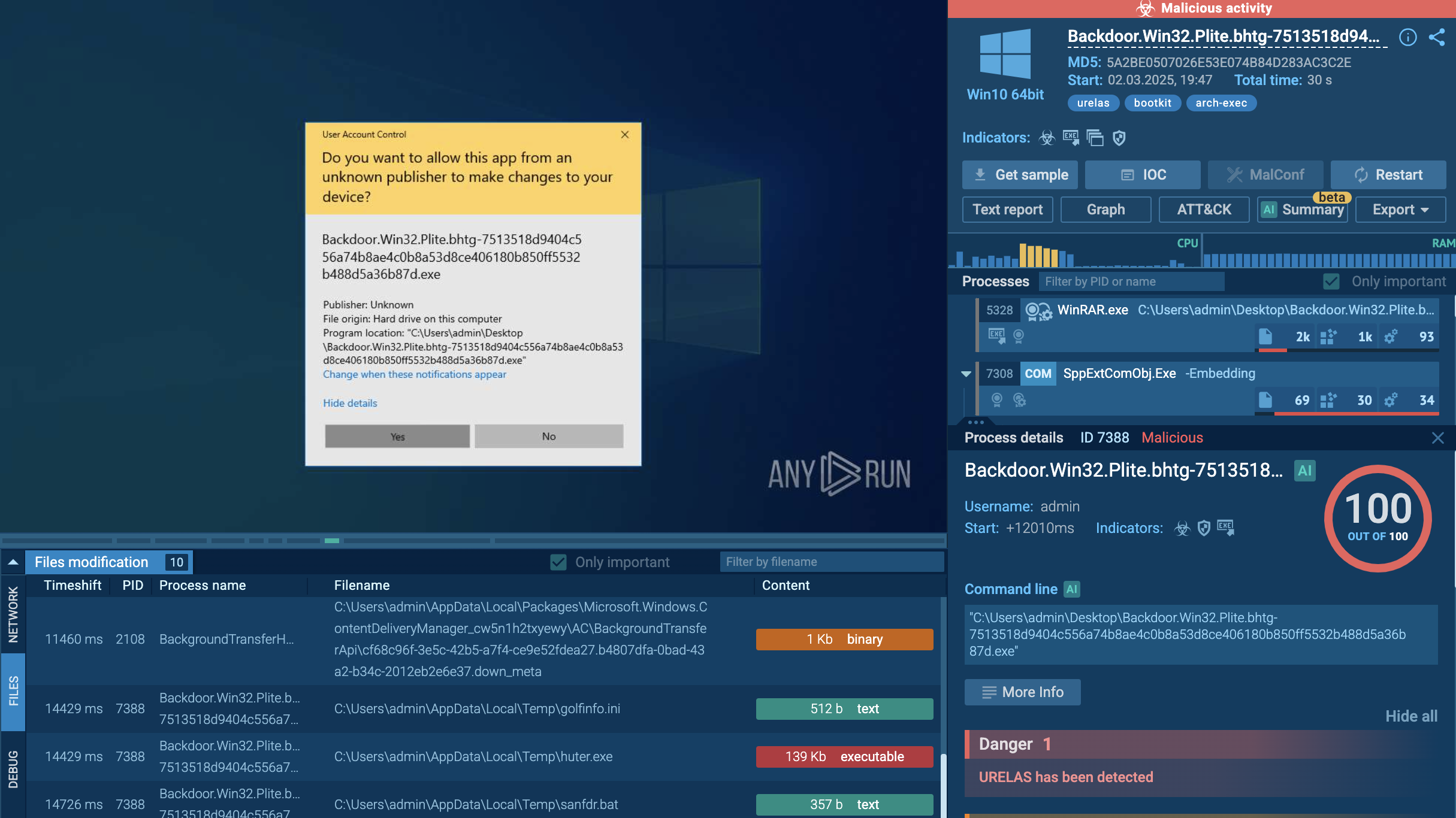
As perpetrators endeavor to conceal their activities, the Mars Stealer employs a deliberately straightforward execution chain to minimize visibility. Consequently, the infected operating system experiences a limited number of processes, and the malware refrains from utilizing system tools. Once the payload infiltrates the compromised system, it promptly initiates its execution.
The analyzed sample initiates a process executing all malicious activities, including data theft and communication with the Command and Control (C&C) server. Malware was detected, and the configuration was successfully extracted.
 Mars Stealer's configuration demonstrated in ANY.RUN
Mars Stealer's configuration demonstrated in ANY.RUN
When it comes to distribution methods, a typical attack in the case of Mars Stealer starts from spam campaigns or fake websites advertising legitimate software. For instance, in 2022, one of the campaigns to distribute Mars Stealer used a website promoting Atomic Wallet, a popular cryptocurrency wallet. After clicking on the “download” button on the website, users would receive a .zip file which contains a sample of Mars Stealer.
The malware was also commonly dropped by loaders, malicious software designed specifically for spreading different malware families on devices they manage to infect. One of the examples here is PrivateLoader.
With malware infections being at an all time high, it becomes important to stay vigilant and exercise caution when encountering any suspicious emails, websites, or software downloads to avoid falling victim to Mars Stealer or similar malware threats, as well as to maintain protection of your infrastructure.
ANY.RUN, a cloud-based sandbox, offers accurate threat detection, along with detailed reports on their technical characteristics. It lets you scan any suspicious file and check potentially malicious URLs to ensure informed decision-making and timely removal of any traces of the malware.
Try ANY.RUN for free – register now!