Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases

Lu0Bot is a Node.js malware that was first discovered in February 2021. It is a type of Trojan that primarily acts as a stealer by responding to commands from a command-and-control (C2) server and transmitting encrypted system data. It can also operate as a DDoS bot. Lu0Bot employs multiple obfuscation techniques to avoid detection and make analysis more difficult.
|
Trojan
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 February, 2021
First seen
:
|
24 April, 2025
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 February, 2021
First seen
:
|
24 April, 2025
Last seen
:
|

 1555
1555
 0
0
 2612
2612
 0
0

 2125
2125
 0
0
Lu0Bot is a trojan that was first observed in 2021. Although less widely used than other trojan malware, such as Agent Tesla, it has the potential to inflict serious damage on infected systems.
A notable feature of Lu0Bot is its use of Node.js, an unusual programming language choice for malware. However, this unconventional approach provides Lu0Bot with versatility compared to most malicious programs that are usually developed using the .NET framework, which is limited to Windows systems.
Despite being a highly capable threat, Lu0Bot has a relatively low level of activity. Currently, its primary function is data harvesting, but it can also be used as a DDoS attack bot and may have other capabilities.
Once Lu0Bot is fully deployed on the system, it can engage in:
Lu0Bot is highly obfuscated, meaning that its code is deliberately made difficult to read and understand in order to prevent or obstruct analysis. It uses several encryption algorithms, including custom ones.
By comparing Lu0Bot samples from 2021 and 2023, it becomes clear that the software is being continuously updated by its developers.
Read a detailed analysis of a Lu0Bot sample in our blog.
In order to see how Lu0Bot operates and collect up-to-date IOCs, let’s examine one of its samples in the ANY.RUN sandbox.
Analyze malware for free in a fully interactive cloud sandbox – sign up now!
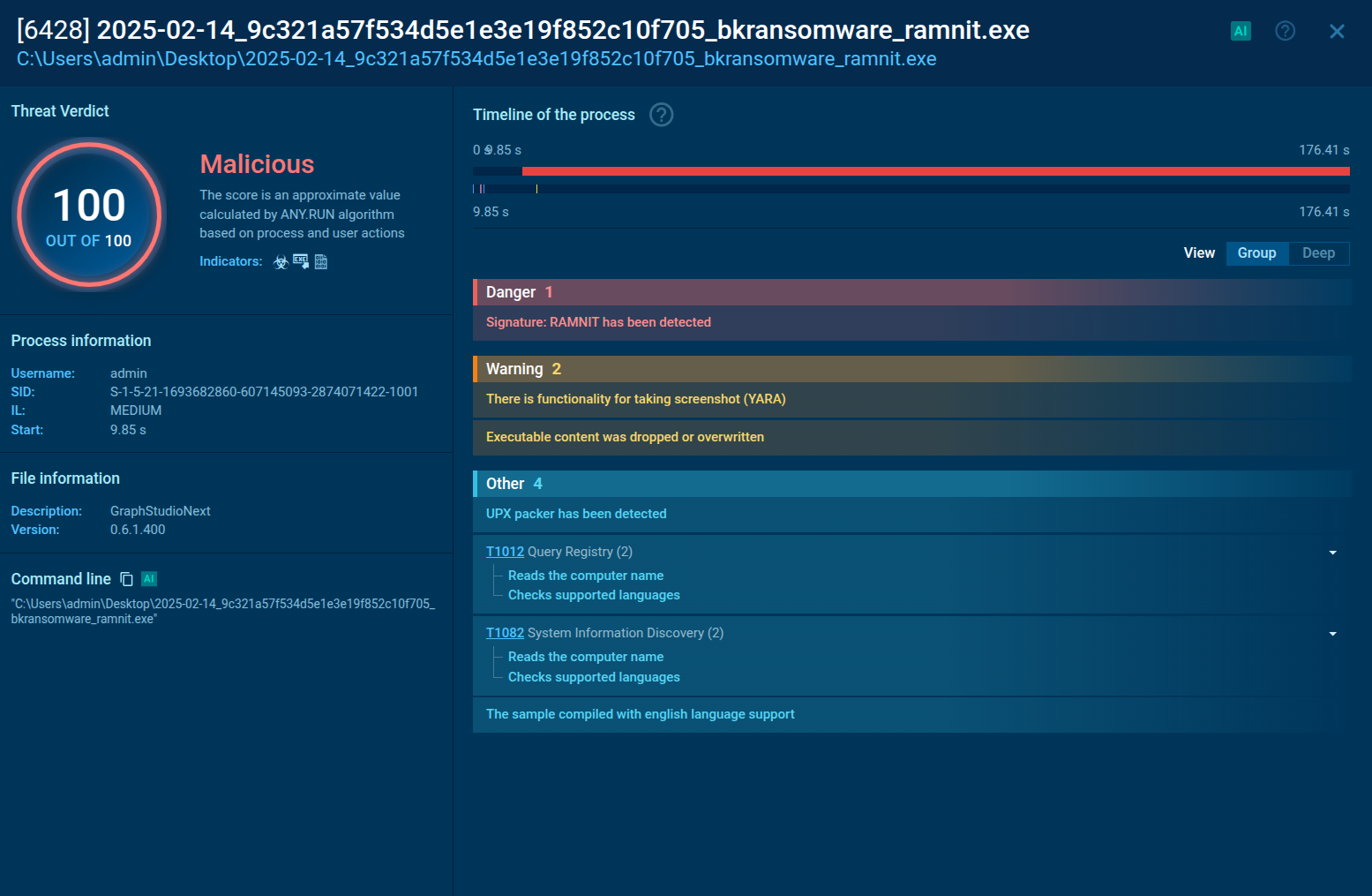
The execution chain of this malware family is relatively straightforward. After the payload executes, it uses CMD to copy and initiate the main malware process. This process is responsible for carrying out all malicious activities, including data theft, C&C server communication, and, in this case, gathering process information using WMIC.EXE.
 Lu0Bot's process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
Lu0Bot's process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
In the early days, Lu0Bot was primarily dropped by GCleaner, a specialized software for deploying second-stage payloads. Yet, today, the main method of delivery for this malware is phishing emails. Essentially, attackers employ various social engineering techniques in order to get their victims to download malicious email attachments or open unsafe links and trigger the infection chain reaction on their systems.
Despite being a known threat, the true scale of Lu0Bot's operations remains unknown. This makes it a dangerous malware capable of dealing a significant blow to any infrastructure, if not addressed proactively. Therefore, organizations must implement proper security measures to prepare for Lu0Bot attacks.
One of the most effective ways to prevent a Lu0Bot attack is to check any incoming files and links, especially those sent by unknown senders, in the ANY.RUN sandbox. It is a malware sandbox that lets you quickly understand if the file or link your are dealing with is malicious or not.
ANY.RUN is fully interactive, enabling you to engage with the infected system like you would on your own computer but in a safe cloud environment to fully understand the behavior of the malware. It also provides comprehensive reports that include IOCs and malware configs.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!.